As a powerhouse that efficiently converts solar energy into electricity, the solar inverter plays a crucial role in making renewable energy usable and accessible for everyday appliances.
The way an inverter works is quite fascinating. It first receives power from the grid or the solar panel. Then using semiconductors, which can be made of silicon or gallium arsenide, it converts this energy from one type of current (DC power) to the other (AC power).
This process of conversion from direct current to alternating current is pivotal in ensuring electrical power can be utilized by appliances at home.
Different types of inverters include sine wave, square wave, and modified sine wave inverters. Sine wave inverters are most commonly used, offering a reliable and efficient solution for powering devices through a solar inverter.
Understanding How Inverters Work

There are three core types of inverters – sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave inverters, each with their unique ability to convert DC power into AC for various inverter system applications.
Belonging to the sine wave category, pure sine wave inverters are renowned for their capability of providing clean, smooth, and reliable power. This type of inverter is perfect for running sensitive electronic devices without any risk of damage or disturbance.
On the other hand, modified sine wave inverters are generally more affordable but may not work as efficiently with certain appliances.
Lastly, square wave inverters, are seldom used due to their limited compatibility with modern devices.
The selection of an inverter should be based on the power needs of your home and the nature of the devices you intend to power. It’s also essential to consider the total energy consumed by these devices, as it directly impacts the choice of inverter.
The Role of Inverters in a Solar Power System
Solar inverters come equipped with advanced features like a direct connection to the grid, battery storage options, and even power outage protection. The latter ensures an uninterrupted AC power supply by transforming the DC power efficiently and maintaining steady voltage and frequency. These inverters are designed to manage and distribute solar power, making your solar power system more reliable.
Among the three types of inverters, the pure sine wave inverter is often hailed as the best option for most home appliances. It provides a continuous, smooth, and uniform power supply, closely mimicking the power from the grid. This type of inverter is ideal for sensitive electronic devices such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and laptops.
Modified sine wave inverters, on the other hand, provide a less uniform but still usable power supply. These inverters are usually more cost-efficient, making them suitable for less sensitive appliances.
The least expensive and least efficient of the three are the square wave inverters. These inverters are not compatible with modified sine wave inverter systems and may cause issues with voltage and frequency.
Key Points About Solar Inverters
- Solar inverters come with advanced features such as direct grid connection, battery storage options, and power outage protection, ensuring a steady and uninterrupted AC power supply.
- The pure sine wave inverter is often considered the best for most home appliances as it provides a continuous, smooth, and uniform power supply, similar to grid power.
- Modified sine wave inverters offer a less uniform but still usable power supply, and are more cost-efficient, making them suitable for less sensitive appliances.
- Square wave inverters, the least expensive and least efficient of the three, are not compatible with modified sine wave inverter systems and may cause voltage and frequency issues.
AC and DC Power: The Conversion Process
A solar inverter converts the direct current produced by solar panels into alternating current for use in homes and businesses. These devices are usually connected to the grid to provide a continuous power supply even during outages.
Modern inverters can also store energy in battery storage systems, ensuring power availability during night hours or power grid failures.
Choosing the right inverter that suits your power needs depends on the type of appliances you want to run and the number of hours of operation.
Varieties of Inverters: Sine Wave
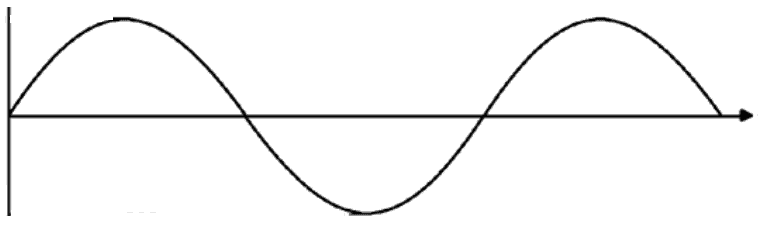
Harnessing solar energy involves more than just using solar panels, it also requires a power inverter to convert the DC electricity produced into usable AC power – A crucial component in this renewable energy source is the inverter system.
Among the different types of inverters, the pure sine wave inverter is recognized for its accuracy and efficiency. It converts the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power, ensuring power quality remains unyielding.
This is particularly beneficial for power-sensitive devices like air conditioners and refrigerators, where the pure sine wave inverter surpasses other inverters in performance and effectiveness
Key Facts About Solar Energy Conversion
- Solar energy conversion requires not only solar panels but also a power inverter.
- The inverter system is a crucial component of this renewable energy source.
- Among different types of inverters, the pure sine wave inverter is known for its accuracy and efficiency.
- The pure sine wave inverter is particularly beneficial for power-sensitive devices like air conditioners and refrigerators.
Square Wave
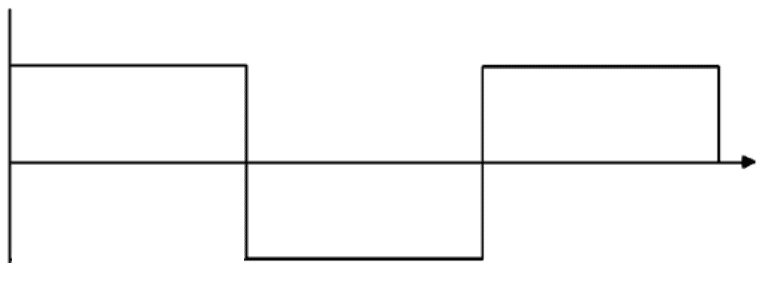
A square wave inverter may not be your best option due to its abrupt transitions, which can lead to power consumption issues. This is especially rampant when used with devices like air conditioners that require a steady waveform and efficient DC power conversion.
However, for less sensitive appliances, a square wave inverter can efficiently serve the purpose.
Modified Sine Wave

Modified Sine Wave inverters work well with most types of appliances and are therefore ideal for homes, offices, and even in certain industrial settings.
It’s important to mention that Modified Sine Wave inverters can cause some devices to run less efficiently. This is due to the less natural waveform that these inverters produce compared to Pure Sine Wave inverters. Particularly sensitive devices may produce more heat or noise due to the slightly uneven current this type of inverter delivers.
Despite this, the cost-saving benefits often outweigh the drawbacks for many users.
Inverters
- Energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness are key factors to consider when choosing an inverter for home use.
- Modified Sine Wave inverters can cause some appliances to run less efficiently due to their less natural waveform, which may result in increased heat or noise in sensitive devices.
- The drawbacks of Modified Sine Wave inverters are often outweighed by their cost-saving benefits for many users.
- The conversion of DC power into usable AC power involves a semiconductor, and the inverter uses a transistor to generate a modified AC output, optimizing overall power consumption.
How Inverters Support Your Home During Power Outages
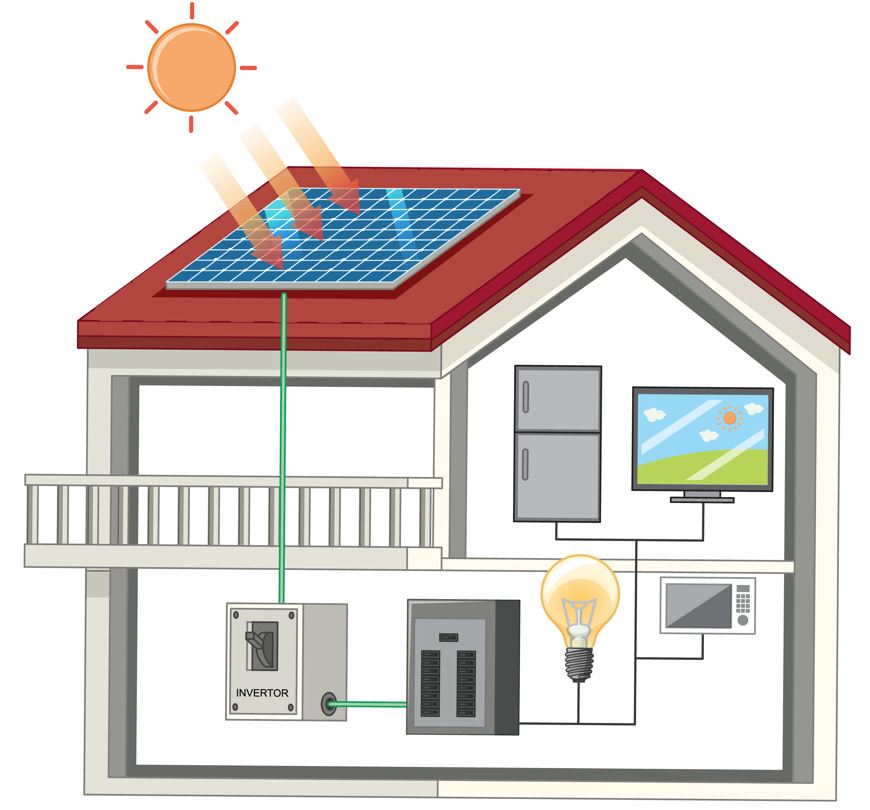
When the lights unexpectedly flicker and stop, leaving you in the quiet darkness of a power outage, a trusty inverter may become your savior. These handy units ensure your refrigerator stays cold and your home stays connected to the grid, all while utilizing stored solar energy. This compact yet mighty gadget provides a shield for your household from electrical interruptions, acting as a crucial unit that ensures key appliances, like your refrigerator, continue working.
Using an inverter helps link your house to a reliable source of energy, often a battery or a generator. Fundamentally, an inverter is an advanced technological device that changes DC power, commonly generated by a generator or battery, into AC power.
This conversion enables your household appliances, which require AC power, to operate adequately even during a power failure. Significantly, there is a type of inverter known as the solar inverter, which is directly connected to the grid. Solar inverters promote sustainable living by exploiting solar energy
Ensuring Proper Connection: How to Set Up The Right Inverter
Various types of inverters exhibit different power consumption patterns and efficiency levels.
For instance, pure sine wave inverters, known for their high efficiency, are ideal for running sensitive electronic appliances, providing a clean energy source that is free from power line disturbances.
On the other hand, modified sine wave inverters can also handle heavy-duty appliances, albeit at a potentially higher energy consumption rate.
The square wave inverters are less common due to their limited efficiency and applicability, yet they serve as an economical choice for basic power needs. They can run simple systems such as lights and tools without the need for complex power conversion mechanisms. It’s crucial to consider how inverters are ideal as an energy source, especially in the face of frequent power outages and rising energy consumption.
Battery storage systems are also an integral component of modern solar power systems. They help store excess energy, which can be used during power outages or when the solar panels cannot generate enough electricity. They ensure a steady energy source regardless of weather conditions or energy consumption levels. This ability to maintain a consistent power supply showcases their importance in the broader renewable energy landscape.
Inverter Type | Efficiency | Applicability | Energy Consumption
Pure Sine Wave Inverters | High | Sensitive Electronic Appliances | Low
Modified Sine Wave Inverters | Medium | Heavy-Duty Appliances | Potentially High
Square Wave Inverters | Low | Basic Power Needs (Lights, Tools) | Low
Maximizing Solar Energy: The Key Role of an Inverter
Inverters are not just limited to power supplies during outages, they also come into play in energy consumption and energy distribution.
In homes connected to the grid, inverters can convert excess solar energy into electricity that’s fed back to the power grid, providing an alternative energy source to conventional power plants.
Modern inverters have also integrated features like voltage and frequency regulation, ensuring the output is safe for all household appliances. These inverters also have real-time monitoring capabilities for performance tracking and diagnosis of potential issues.
Essentials of an Inverter System: From Solar Panels to AC Output
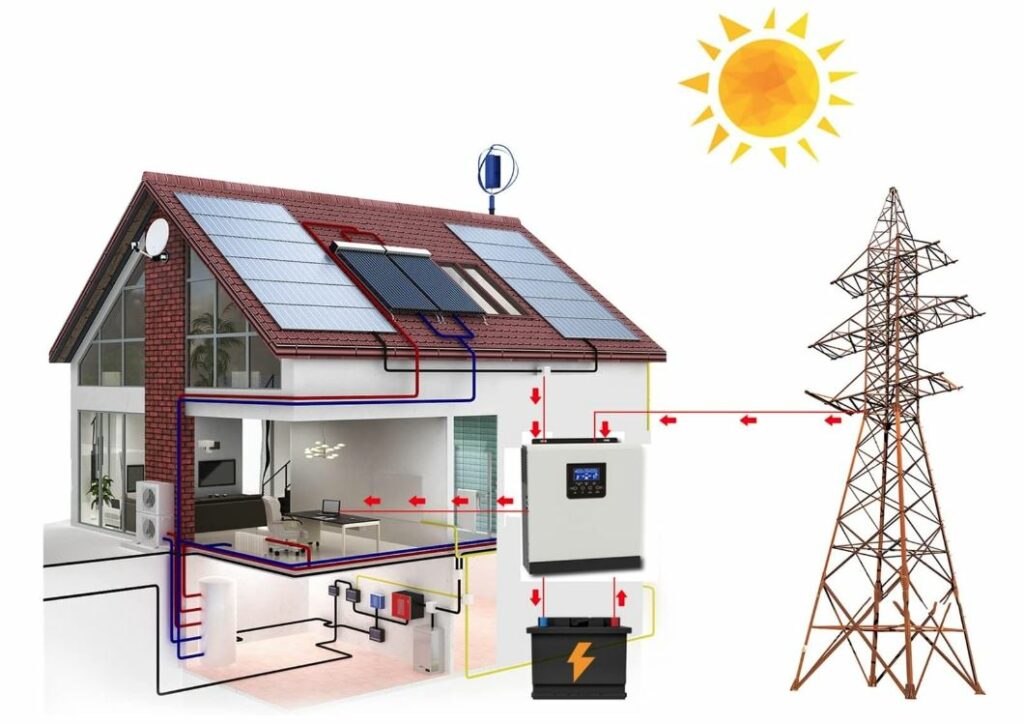
Power outages can cause significant disruption to home appliances, but installing one of the three types of inverters can help store energy and meet power needs using clean, photovoltaic grid power. A battery storage system can also recharge itself from the grid or renewable energy sources like solar panels, making it an excellent backup power option.
Understanding your power consumption and needs will help you choose an inverter system that suits your lifestyle and energy requirements best. Knowing how much energy your home consumes allows you to choose an inverter with the capacity to handle the total power needed, including all essential appliances and equipment.
Different types of inverters work best for specific applications. For example, if you have a solar power system at home, a solar inverter is ideal. Solar inverters are designed to handle the power output from solar panels, converting it from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), the form of energy most home appliances use.
Modern inverters connected to the grid can provide clean energy to your home and return excess power to the grid, reducing overall energy consumption and meeting your power needs with efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
Key Points About Inverters and Power Outages
- Inverters can store energy and meet power needs using clean, photovoltaic grid power, acting as a backup during power outages.
- The inverter’s capacity should be able to handle the total power needs of your home, including all essential appliances and equipment.
- Solar inverters are ideal for homes with solar power systems, as they convert the power output from solar panels from DC to AC.
- Modern inverters connected to the grid can provide clean energy to your home and return excess power to the grid, reducing overall energy consumption.
Power Consumption and Inverters: What You Need to Know
Power supply to your home can be greatly optimized with modern inverters and battery storage systems.
There are three types of inverters: sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave. Sine wave inverters provide a smooth, clean energy source that closely mimics the power from the grid. They are ideal for sensitive devices and appliances, such as refrigerators or air conditioners.
Modified sine wave inverters, on the other hand, provide a less smooth waveform, which is adequate for most household appliances. These inverters tend to be less expensive and are often used when the cost is a significant factor.
Lastly, square wave inverters produce a very simple and rough form of AC. They are not as common as the other two, as their power quality is much lower. They are typically used in very simple systems, such as basic power tools.
It’s important to choose an inverter that suits your needs. Determining this depends on the type of devices or battery power required, and their ability to recharge from modern inverters or draw electrical power directly from the grid.
Inverter Systems
The most common types of inverter systems are pure sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave inverters. The pure sine wave inverter produces a smooth, uninterrupted flow of current similar to the grid power supply. One inverter, for instance, can power an entire home with this type of energy delivery system.
Without these systems in place, the entire home is susceptible to interruptions and outages, leaving its consumers powerless when a single inverter used in a system fails to convert direct current effectively.
The inverter system, aside from being your mini power station, also ensures clean, renewable energy is maximized. Solar power, once harnessed by solar panels, is stored in the battery inverter in the form of direct current (DC). When demand arises, the inverter converts this DC into alternating current (AC) ready for use. This process is seamless and automatic, delivering power exactly when you need it.
Inverter Systems
- The inverter system acts as a mini power station and ensures the maximization of clean, renewable energy.
- Solar energy, once harnessed by solar panels, is stored in the battery inverter as direct current (DC). The inverter then converts this DC into alternating current (AC) when needed.
- The conversion process from DC to AC is seamless and automatic, supplying power exactly when required.
- Common types of inverters include pure sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave inverters. The pure sine wave inverter produces a smooth, uninterrupted flow of current, similar to the grid power supply.
Making the Right Choice: Identifying the Ideal Inverter for Your Home
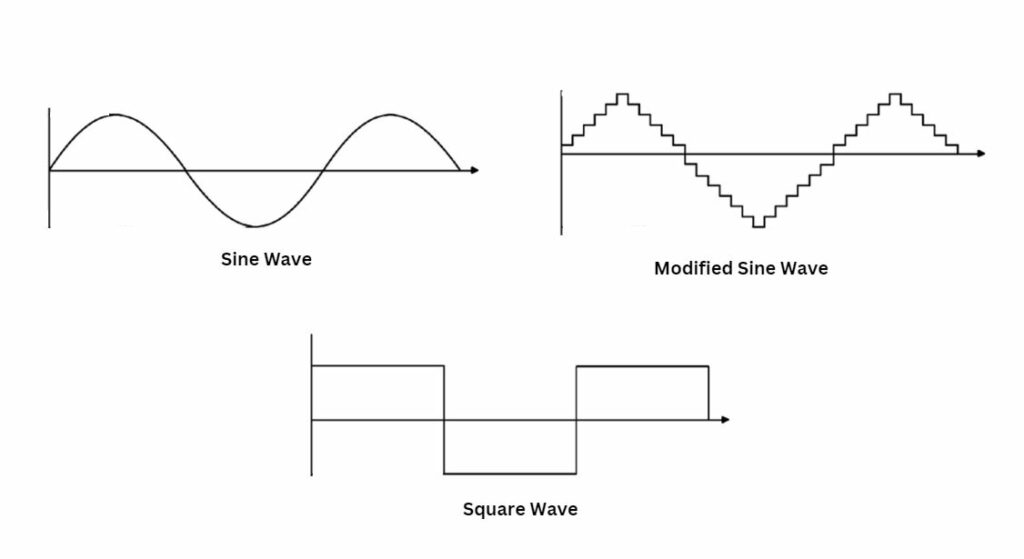
The three main types of inverters are sine wave inverters, modified sine wave inverters, and square wave inverters. These types are defined by the type of waveform they generate – a factor that significantly influences the performance of the appliances connected to the inverter.
Sine wave inverters, also known as pure sine wave inverters, generate a waveform identical to the one supplied by the power grid. This inverter type is ideal for running sensitive electronic equipment that requires a high-quality waveform to function correctly.
Modified sine wave inverters generate a waveform that is suitable for conversion to AC, thus providing power to power tools and connecting to renewable energy sources in the power grid.
Square wave inverters are less common and serve as an economical choice for basic power needs.
Modern Inverters and Renewable Energy: Pushing Towards a Sustainable Future
The inverter type best suited for the household depends on both the AC power needs of the home (or business) and the nature of the DC source.
The pure sine wave inverter, for instance, is ideal for running sensitive electronics and appliances as it produces a smooth, consistent AC waveform.
The modified sine wave inverter, on the other hand, is more commonly used for less sensitive devices, given its simpler, less expensive design. It’s less energy-efficient compared to the pure sine wave inverter and could potentially cause a buzzing noise in some appliances.
The square wave inverter, the simplest and least expensive of the three types, is less commonly used today due to reduced efficiency and increased power consumption. It is the least energy-efficient of the three and is best suited for small, basic applications, such as running power tools.
Key Facts About Inverters
- Control characteristics of inverters ensure reliable AC power supply during grid outages, playing a crucial role in maintaining the total energy supply.
- The type of inverter suitable for a particular application depends on the AC power needs and the nature of the DC source.
- Pure sine wave inverters are ideal for running sensitive electronics and appliances due to their smooth, consistent AC waveform.
- Modified sine wave inverters are more commonly used for less sensitive devices due to their simpler, less expensive design, but they are less energy-efficient.
- Square wave inverters, though the simplest and least expensive, are less commonly used today due to their reduced efficiency and increased power consumption. They are best for small, basic applications like running power tools.