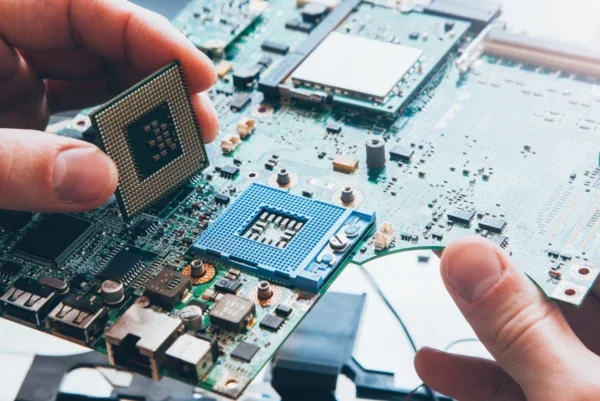
Upgrading your laptop’s CPU requires careful planning, assessment of your laptop’s technical specifications, and a fair degree of technical expertise. However difficult it may seem at first, it is well worth the effort as this upgrade can significantly increase processing speed and performance. If a CPU upgrade is feasible, the next challenge is ensuring that the new CPU is compatible with your laptop’s motherboard and power supply.
In addition to ensuring compatibility, proper installation and applying the right amount of thermal paste are crucial to prevent overheating and potential damage.
If an upgrade is not possible or too complex, you may consider alternatives to increase your laptop’s processing power.
Adding more RAM, installing an SSD, or even buying a new laptop might be more practical and cost-effective for some users.
Upgrading Your Laptop CPU: What You Need to Know
It is crucial to consider many factors before deciding to upgrade a laptop CPU as this often requires a substantial investment. Especially if in your case an entirely new motherboard or even a new laptop is needed. The first is to check if your laptop processor is socketed. If so, a CPU upgrade might be feasible.
The process involves carefully removing the old CPU and replacing it with a new one. However, even with a socketed CPU, compatibility is a crucial factor.
It is necessary to ensure the new CPU matches your laptop’s socket and motherboard. The laptop’s thermal management capability must be able to handle the heat generated by the new processor.
The laptop must also have enough power supply to support the new CPU. Nonetheless, the majority of modern laptops do not feature a socketed CPU but instead, use a soldered-on processor which makes it almost impossible to upgrade a laptop CPU.
Can You Upgrade a Desktop Processor?

An incorrectly installed CPU can cause significant harm to your desktop computer. Because of this, always consider professional assistance when upgrading your laptop processor. Also, consider the cost as a powerful CPU can be an expensive component. Another consideration is whether your system has sufficient power supply and cooling mechanisms to support a new, potentially more powerful processor.
As for laptops, the possibility of a CPU upgrade can be more complex. This is because many modern laptops have their CPUs soldered onto the motherboard, making it impossible to upgrade the processor without upgrading the entire motherboard. When you’re looking to increase your laptop’s performance, it may be more beneficial to consider upgrading other components such as the Random Access Memory (RAM) or the hard drive.
While desktop computers typically allow for CPU upgrades, laptops may not provide such flexibility. Before attempting a CPU upgrade, it’s essential to understand the specific type of laptop processor your device uses and confirm whether it’s possible to upgrade the laptop’s CPU.
Key Points About CPU Upgrades
- An incorrectly installed CPU can cause significant damage to your computer, so professional assistance is recommended when upgrading.
- Powerful CPUs can be expensive, and your system needs to have sufficient power supply and cooling mechanisms to support them.
- Upgrading the CPU on a laptop can be more complex due to the CPU often being soldered onto the motherboard. In such cases, it may be more beneficial to upgrade other components like RAM or the hard drive.
- Desktop computers typically allow for CPU upgrades, but laptops may not provide such flexibility. Therefore, it’s essential to understand your laptop’s specific processor type before attempting an upgrade.
Understanding Laptop CPU Upgradeability
The task of upgrading a laptop’s hardware cannot be undertaken lightly or by inexperienced users, especially when you consider upgrading crucial components like the CPU from an i3 to an i7 or increasing the RAM and hard drive capacity. In contrast to desktop computers, most laptop processors are not socketed.
Rather than being detachable components that can be swapped out, they are meticulously integrated into the laptop’s motherboard. This integration ensures that the laptop operates efficiently within its compact design.
The downside, however, is that the processor becomes non-upgradeable; a fact that many laptop users discover to their dismay, making it impossible to upgrade a laptop’s CPU easily. However, there are still laptops in the market that allow CPU upgrades, though they are few and far between.
These are typically high-end laptops that follow a modular design, providing a certain degree of customization potential.
How to Identify Your Laptop Processor

For when you are looking to improve your laptop’s performance, consider upgrading elements such as the processor, motherboard, and CPU. However, whether or not these upgrades are possible largely depends on the specific laptop model.
In general, for modern laptops, the CPU is usually soldered directly onto the motherboard, making it rather difficult, if not impossible, to upgrade.
Yet, there are exceptions. Certain older laptop models or high-end gaming laptops may utilize a socketed CPU which means the processor can be removed and replaced.
This process requires technical expertise and can potentially void the warranty of your laptop. Upgrading a laptop’s CPU also involves other considerations. For instance, the new CPU must be compatible with your laptop’s motherboard, otherwise, the upgrade process may involve complex soldering work or may not be possible at all.
Key Points About Laptop CPU Upgrades
- In general, the CPUs of modern laptops are soldered directly onto the motherboard, making upgrades difficult or impossible.
- Some older or high-end gaming laptops may have a socketed CPU, which can be removed and replaced.
- Upgrading a laptop’s CPU requires technical expertise and could potentially void the laptop’s warranty.
- The new CPU must be compatible with the laptop’s motherboard, otherwise, the upgrade process may involve complex soldering work or may not be possible.
Is it Possible to Upgrade Your Laptop Processor?

Diving deeper into the variety of options when it comes to laptop upgrades, let’s discuss replacing an existing i3, i5, or i7 processor in your laptop. The key to a successful processor upgrade lies in understanding the complexities of the Intel socket design and the laptop’s own BIOS settings. While it’s technically possible to substitute the CPU, the feasibility of this operation is strongly linked to the laptop’s make and model.
Most modern laptops have the CPU conveniently soldered to the motherboard, which limits the scope for future upgrades significantly. There are still exceptions where the processor is socketed, thus enabling an upgrade.
Certain brands or models accommodate the niche audience who regularly update their hardware. Nonetheless, attempting such an operation presents its unique challenges.
There’s considerable risk associated with upgrading your laptop’s CPU, particularly when the task is undertaken without suitable technical skills. The risks are numerous and should not be overlooked when deciding to upgrade the CPU or RAM on modern laptops and desktops.
The Role of the Motherboard in CPU Upgrades
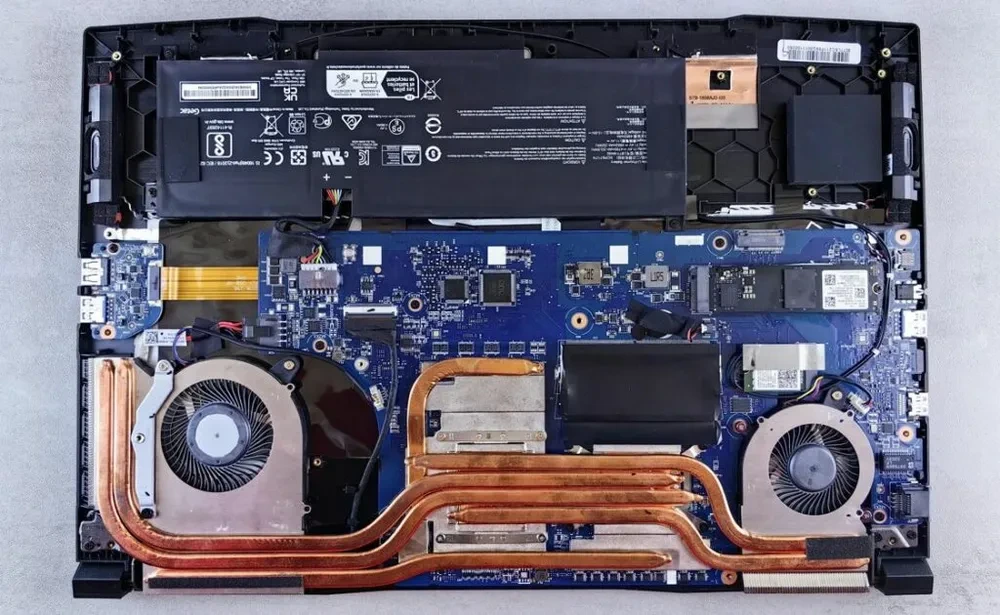
The motherboard connects all internal components such as the CPU, RAM, and the hard drive. Because of this, Its role in CPU upgrading is significant.
The BIOS, also known as the Basic Input Output System, is the software that enables the motherboard to interact with the hardware.This software needs to be compatible with the new CPU to ensure the successful upgrading of a laptop CPU .
Before diving into an upgrade, it is worth considering whether upgrading a desktop PC would be a more feasible and cost-effective solution.
Unlike laptops, desktop computers tend to have a more modular design, making components such as the CPU easier to access and replace. For individuals who are entirely reliant on the portability of laptops, replacing the laptop itself may be the only viable option. This is especially true if the current laptop’s processor is soldered onto the motherboard, preventing a CPU upgrade or the addition of a new GPU or SSD.
CPU Upgrading
- The BIOS software plays a crucial role in CPU upgrading as it enables the motherboard to interact with the new CPU.
- Upgrading a desktop PC might be more cost-effective and feasible due to its modular design that makes components like the CPU easier to access and replace.
- For individuals who rely on the portability of laptops, CPU upgrading might be the only viable option, especially if the current laptop’s processor is soldered onto the motherboard.
- Despite the challenges, upgrading the CPU, SSD, and GPU of a laptop can significantly enhance its performance and extend its lifespan.
The Difference Between Soldered and Socketed CPUs

Knowing the distinction between soldered and socketed Central Processing Units (CPUs) is paramount in understanding why you cannot upgrade your laptop’s processor on certain devices. These two types of CPUs, which act as the brains of your laptop’s processor, have marked differences in their design, functionality, and upgrading capacity.
A soldered CPU is permanently fixed to the motherboard of your laptop, ruling out the possibility that you of upgrading it.
In contrast, a socketed CPU is placed in a removable socket on the motherboard of your laptop, making it possible to upgrade your laptop’s processor.
While most modern laptops have soldered CPUs, many high-end models still have socketed options for more customization.
How to Choose a New CPU for Your Laptop
Newer, high-end models present a more modular design that might allow for easier upgrades, so if you’re looking to replace an older laptop, you may want to consider upgrading to a laptop with an Intel i7 CPU. With this in mind, the compatibility of the CPU socket with your selected processor is still a crucial consideration.
Unlike desktop computers, where it is typically possible to select a different CPU and swap it out, laptop CPUs are often soldered onto the motherboard. This makes upgrading them more difficult, and not all laptops allow for this.
While the technical expertise required for a CPU upgrade in a laptop is substantial, the limitation is primarily due to manufacturers’ design choices. In a bid to conserve space and ensure efficient thermal management, modern laptop manufacturers have started incorporating Intel’s i7 CPU into their designs, making their products both compact and powerful.
Laptop CPU Upgrades
- Newer laptop models are designed to be more modular, which could potentially allow for easier hardware upgrades.
- Upgrading a laptop’s CPU is not always possible because they are often soldered onto the motherboard.
- The ability to upgrade a laptop’s CPU is primarily limited by the manufacturers’ design choices, not the technical expertise required.
- Modern laptop manufacturers have started incorporating Intel’s i7 CPU into their designs for better performance and efficient thermal management.
Preparing Your Laptop for a CPU Upgrade

Tasks such as upgrading the processor that’s soldered onto the motherboard need to be performed by a professional to avoid any long-term issues. It may also be a costly endeavor, especially if the laptop requires a specific type of CPU that is not widely available or if you have to hire a professional for the upgrade.
Instead of risking these complications, some laptop users opt for alternative methods to increase processing power. These can include adding more RAM, replacing the hard drive with a solid-state drive (SSD), or even using an external GPU for enhanced graphical performance.
In some cases, however, an upgrade might not be enough to meet your needs, especially if you’re dealing with an older laptop. Buying a new laptop, while more expensive upfront, can offer a longer-term solution and better performance overall. To summarize, the feasibility and worth of upgrading the processor or buying a new laptop largely depends on the type of CPU currently soldered onto the motherboard and the computing needs of the laptop user.
The Process of Upgrading Your Laptop Processor
Upgrading a laptop processor can have a variety of benefits, however, it’s essential to ensure that the new processor is compatible with the existing CPU socket, you are applying thermal paste correctly, and you have a suitable screwdriver for the job. While it might be tempting to aim for a more powerful CPU, such as an i7 or i5, it’s essential to consider if your laptop is upgradeable at all.
Most modern laptops don’t offer the flexibility for CPU upgrades due to their compact and intricate designs, as CPUs are often soldered directly onto the CPU socket. If you’re considering an upgrade, ask yourself: does the additional processing power justify the risks associated with upgrading hardware on a device that was not originally designed to be upgradeable? In most cases, it’s more economically viable and less risky to invest in a new laptop than to upgrade an older one.
| Factors to Consider | Implications |
|---|---|
| Processor Compatibility | Ensure that the new processor is compatible with the existing CPU socket to avoid damaging your laptop. |
| Appropriate Tools | Having a suitable screwdriver and applying thermal paste correctly are crucial steps in the process. |
| Manufacturer’s Upgradeability | Most modern laptops are not designed to be upgradeable due to their compact and intricate designs. |
| Cost and Risk Analysis | Consider if the gain in processing power justifies the costs and risks associated with upgrading hardware. |
Common FAQs About Laptop CPU Upgrades
Upgrading laptop CPUs is a complex process because CPUs are typically soldered into laptops, and upgrading them requires significant technical expertise. Various factors dictate the feasibility of laptop CPU upgrades.
While many contemporary laptops have CPUs that are soldered onto the motherboard, seeming to make an upgrade impossible, several laptop models still provide socketed CPUs that are suitable for modification.
It’s important to consider the balance between the desired processing power and potential risks, especially for laptops that manufacturers do not explicitly identify as ‘upgradeable’.
When to Consider Buying a New Laptop Instead of Upgrading
If you’re looking for more processing power, it’s important to consider the capabilities of modern laptops.
A mid-range laptop with an i5 or i7 CPU might easily handle tasks that an older laptop with an upgraded external hard drive struggles with. If your device is still relatively new and only requires a memory boost, upgrading the RAM or SSD might be the most economical solution. Ultimately, the decision to upgrade to a newer laptop boasting an 11th or 12th gen power supply depends on the user’s need for a more powerful and efficient computer, amplified storage capacity with an external hard drive, and the convenience offered by a modular design for easy troubleshooting or computer repair.
Laptop Upgrades
- Item 1: The CPUs in newer laptops are soldered directly onto the motherboard, making it impossible to upgrade the processor.
- Item 2: Laptop manufacturers design their devices to work optimally with a specific CPU, so using a different one could lead to performance issues or damage.
- Item 3: A mid-range laptop with an i5 or i7 CPU can often handle tasks more efficiently than an older laptop with an upgraded external hard drive.
- Item 4: Upgrading the RAM or SSD can be a more economical solution for boosting the performance of a relatively new device.